Translate this page into:
George N. Papanicolaou- A tribute

*Corresponding author: Dr. Meherbano Kamal, Department of Pathology, Government Medical College, Nagpur, Maharashtra, India. dr.mmkamal@gmail.com
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
How to cite this article: Kamal M. George N. Papanicolaou- A tribute. CytoJournal 2022;19:20.

GEORGE N. PAPANICOLAOU- A TRIBUTE
Any cytology event or writings are incomplete without knowing about the Father of Cytopathology, Dr. George Nicholas Papinocolaou, MD, PhD (1883–1962). He was born in a small coastal town of Kymi, on the Greek island of Evia. While still a medicine graduate, he had decided not to follow the footsteps of his father who was a general practitioner and was at 1 time mayor of the town. Dr. George Papanicolaou graduated in medicine from the University of Athens in 1904. He acquired a doctorate in philosophy in natural sciences from the University of Munich and served in the Greek Army during the Balkan wars. Here, he came in contact with the Americans and with the hope of better prospects of launching a scientific career, the Papanicolaou couple shifted to New York in 1913 and began research on the estrous cycles of mammals, using cellular samples from the vagina of guinea pigs. Later he extended his work to humans and inevitably, received vaginal smears from women suffering from cervical cancer. This is how he stumbled on cancer cells. He was not searching for them – instead he observed and recognized them serendipitously.[1]
As is true for many important scientific observations, this diagnostic examination was poorly received initially. Papanicolaou’s contemporaries saw no reason to change from diagnostic biopsy of the relatively accessible cervix to the smear technique. In fact, it was not until Papanicolaou received the support of Joseph Hinsey, and the Chairman of Anatomy at Cornell in 1939, that he laid aside his endocrinologic studies and began full time pursuit of the smear method for cancer detection. As a result of Papanicolaou’s collaboration with Herbert F Traut, a pathologist with special interest in gynecologic material, seminal publications in 1941 and 1943 launched the era of development and expansion of cytopathology. This era saw the advent of screening for cervical cancer. In 1954, Papanicolaou published his magnum opus, the comprehensive Atlas of Exfoliative Cytology. The Pap test fulfilled the need of a simple and inexpensive method of examining large numbers of prospective cancer bearers that existed in all populations around the globe. Although Dr. Papanicolaou formally retired from Cornell University in 1951, his activities continued undiminished until his death in 1962, at the age of 77 yrs.[2]
Papanicolaou’s contribution to the field of cytopathology was two-fold: he recognized the importance of wet fixation and he began systematically to accumulate examples of cancer cells in vaginal smears. These sketches of normal and abnormal vaginal and cervical cells [Figure 1a and b] have stood the test of time and are as complete even today. They are both the foundation and the methodology for meaningful cytologic literature. The woman behind this man was his wife Andromahi Mavrogeni who was a longtime assistant in his laboratory [Figure 2]. The fact that, the Papanicolaou’s test has been modified so little during the greater part of its existence is surely a tribute to the insight and inventiveness of this scientist couple. Awards and accolades naturally followed as a tribute to their untiring efforts but the highest honor came in when the scientific community at large decided to name cervical cytology as “The Pap smear.”[3]
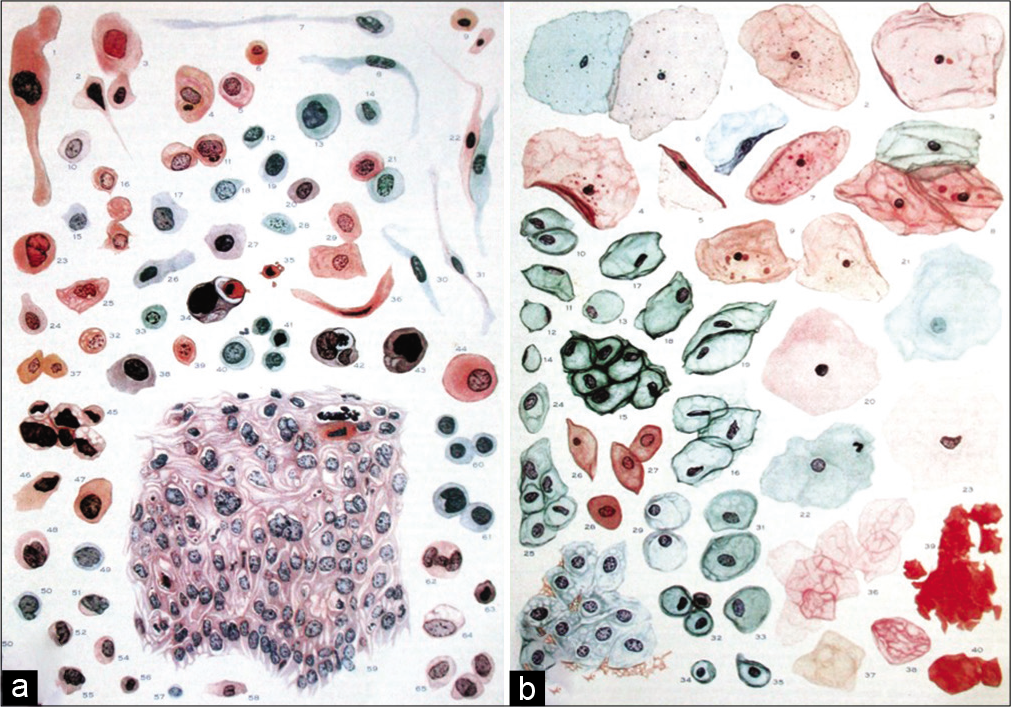
- (a and b) Sketches of normal and abnormal cervicovaginal cells.
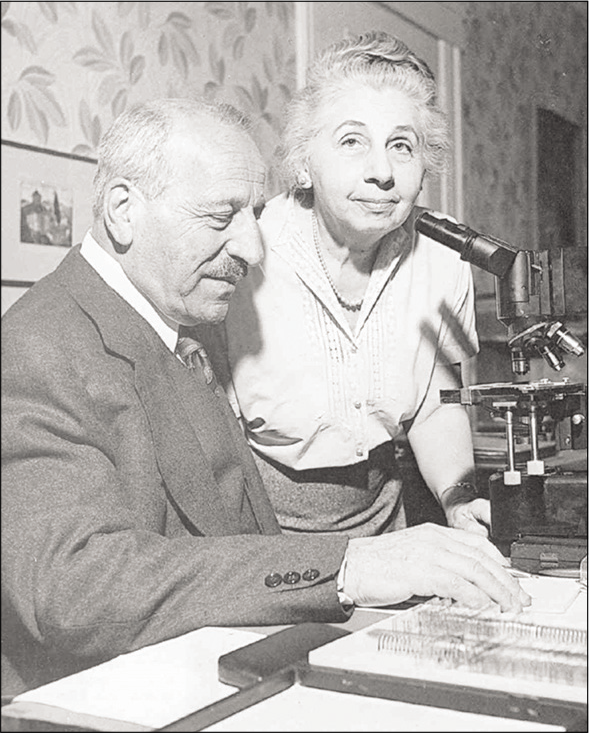

- Dr. Papanicolaou with his wife Andromahi Mavrogeni.
Disciples of Papanicolaou’s smear examination assimilated his teachings and inaugurated their own studies [Figure 3]. A number of future cytopathologists visited his laboratory and many remained for protracted periods, including Leopold Koss, George Wied, and James Reagan. These stalwarts have played a major role in developing cytopathology as a subspecialty of pathology and also in maintaining high standards in cytopathology by their educational and research activities. In 1983, the town of Kymi along with Greek government and University of Athens, celebrated the 100th birth anniversary of Papanicolaou. The United States similarly honored its famous citizen in 1978 and in 1984 Cyprus issued a stamp depicting both Drs. Mr. and Mrs. Papanicolaou [Figure 4].
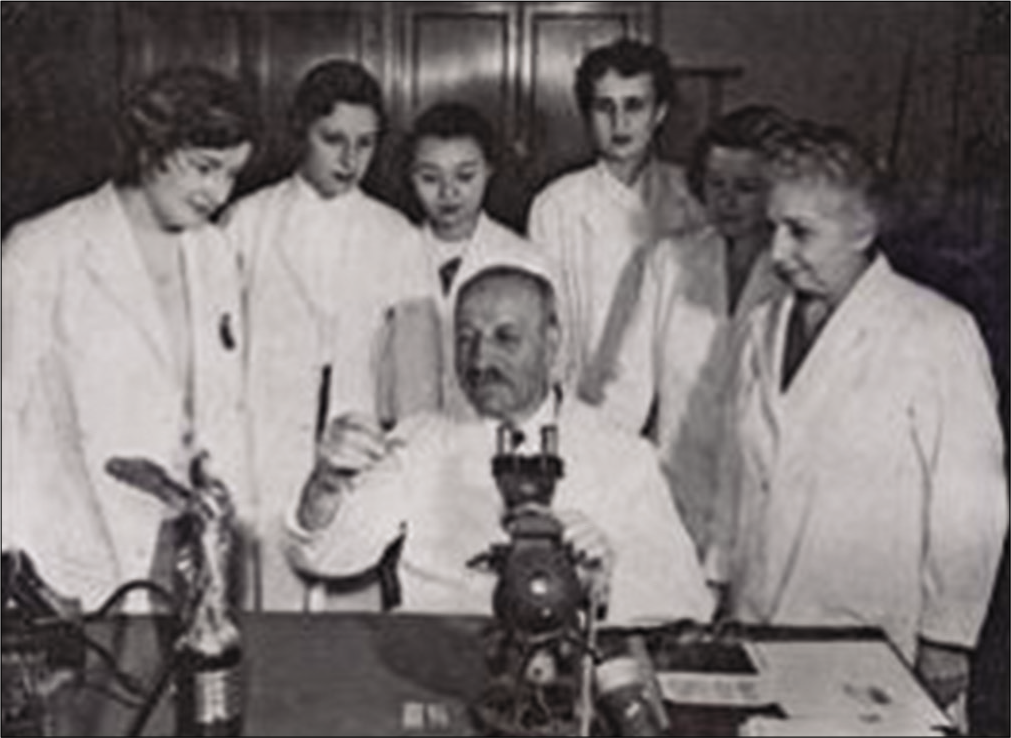

- Disciples of Dr. Papanicolaou learning from his teaching sessions.

- (a and b) United States postage stamp issued in 1980 honoring Dr. G. N. Papanicolaou and the Pap test.
The revolutionary discovery of the “The Pap smear” in the early 20th century and its role in diagnosing & preventing cancer cervix began to arouse worldwide medical attention. A massive cytology screening project using the Pap smear was initiated in 1956 in Jefferson County that lasted for 16 years. When the records of this screening programme suggested that the death rate dropped from 23.7 to 10.2/ lac, the WHO announced, in 1969, that cancer cervix was a preventable disease. Unfortunately, there is no significant change in death rates among the populations of the relatively unscreened women in the developing world. “Preventable but yet not prevented” is the reality today!!! Despite its accomplishments, the Pap test is an endangered species. Will it go the way of the dinosaur, or can we prevent the extinction of this remarkable investigative device?
ABBREVIATIONS IN ALPHABETICAL ORDER
WHO – World Health Organisation.
References
- The papanicolaou smear a brief historical perspective and where we are today. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1997;121:205-9.
- [Google Scholar]
- George Nicholas Papanicolaou, May 13, 1883-February 19, 1962. Acta Cytol. 1962;6:483-6.
- [Google Scholar]
- Diagnostic Cytopathology: Expert Consult: Online and Print Winifred Gray; Gabrijela Kocjan Download B-OK. Available from: https://ru.b-ok2.org/book/3591876/fb517c [Last accessed on 2021 Aug 24]
- [Google Scholar]







