Translate this page into:
Announcement of first time Cytojournal impact factor for 2012 coincides with Cytojournal decade celebration (2004-2013)
*Corresponding author
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Unported, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
This article was originally published by Medknow Publications & Media Pvt Ltd and was migrated to Scientific Scholar after the change of Publisher.
Dear Authors, Peer Reviewers, and Readers,
On behalf of the Cytopathology Foundation Inc., (CF) and the CytoJournal editorial board, we are communicating the recently announced 2012 impact factor (IF) of 1.2 for CytoJournal.[1] This numerical indicator has been long awaited by authors, as many institutions use IF to determine preferences for publication metrics. However, as all CytoJournal readers and authors are aware,[2] there are many additional quality metrics for journals and authors. CytoJournal was launched in 2004 and due to the benefits of internet and open access [Figure 1], since that time many of its metrics have been significantly high [Table 1, Figure 2].[23456] The recently assigned IF of 1.2, announced during our decade celebration (2004-2013) [Figure 3] is yet another additional parameter indicating journal quality.

- Publishing with old traditional method (a) versus open access (b) (Modified from open access publication-CytoJournal 2006; 3:5).(2)
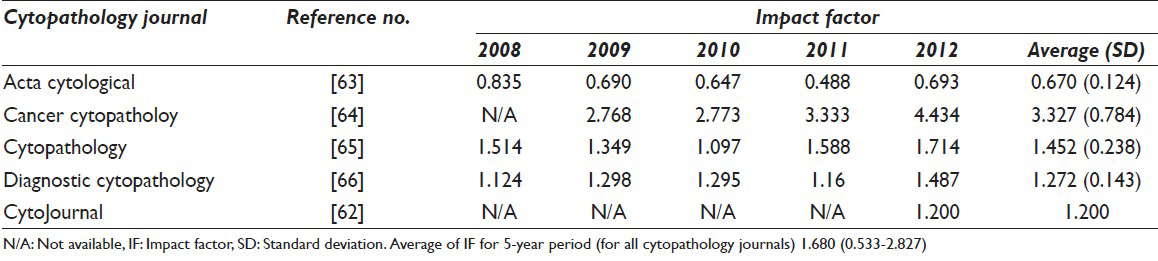
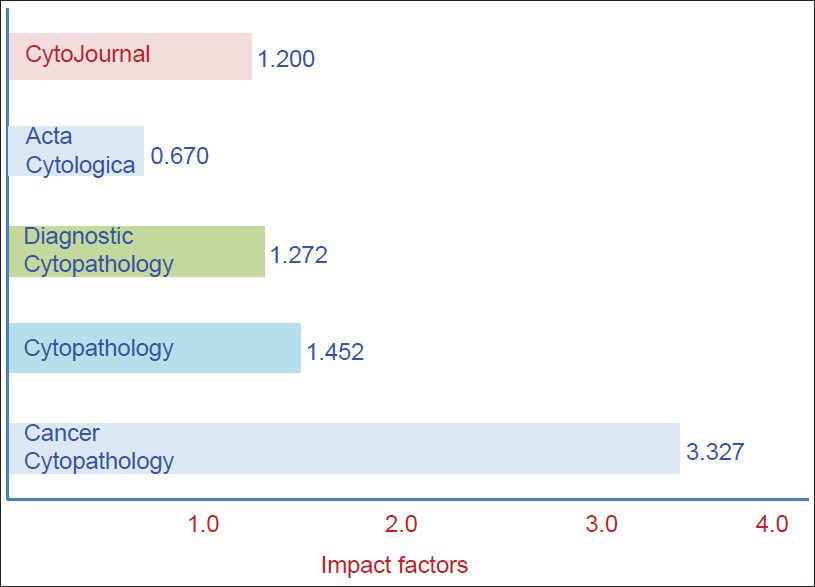
- Impact factors (average for 5 years-2008 through 2012, Table 1) for sentinel peer reviewed cytopathology journals

- CytoJournal decade celebration (2004-2013) of open access in cytopathology
It is the uncompromising efforts of CytoJournal's peer reviewers and the consistent commitment from devoted authors that make all CytoJournal articles suitable for the widest circulation. This process is profoundly facilitated by the open access charter of CytoJournal [Figure 1].[278910] As reported by many scholars, open access charter increases the number of citations per article with an ultimately positive impact for individual authors, CytoJournal, and global readership.[3456]
The 2012 IF for CytoJournal was calculated based on citations from 2010[11121314151617181920212223242526272829303132333435363738] to 2011[3940414243444546474849505152535455565758596061] CytoJournal publications within the articles from indexed journals published in 2012.[1] Considering the trend over 5 years (2008-2012), CytoJournal's IF of 1.2 for 2012 is comparable with the other peer reviewed cytopathology journals [Table 1 and Figure 2].[6263646566] With increasing interest, visibility and access to the readers, as well as copyright retention benefits to the authors, the IF should rise even further over the coming years. The 2012 CytoJournal articles cited during 2013 will contribute to the forthcoming IF for 2013.[6768697071727374757677787980818283848586878889909192]
It is observed that the work of authors who publish in open access journals with free global access is more visible and therefore has increased citation rates for all good quality articles (personal experience, 3-6). As the number of citations is considered an important quality metric, it brings more rewards to the individual authors with expedited career trajectories. In addition, “the creative common license”[93] for all the work published in open access allows authors to retain their copyright in the public domain. This gives them easy and hassle free access to their published material (such as tables and figures) so that they and their colleagues can incorporate such material back into their future works (like in textbooks), with only a citation of the original work needed.[93]
Currently with support from CF, CytoJournal is the only peer reviewed, cytopathology journal that offers this highly beneficial, revolutionary, open access platform to all cytopathology scholars across the globe.[94] An article publication cost (APC) of $ 1,500 for publishing the manuscripts accepted after completion of peer review process is required to accomplish the goal of a self-sustainable publication model. However, with courtesy of the CF, the entire APC of $1,500 is completely waived for all CF members (annual membership is $50 and full CF membership for life is only $1,000, with both dues reduced to 40% for members in developing countries).[95]
We would like to thank the CytoJournal editorial board and its peer reviewers for their high quality editorial support. We also thank Wolters Kluwer/Medknow[96] for their publishing support with a commitment to the open access charter in collaboration with the CF.
Congratulations are also extended to all of the authors for their achievements in attracting high citation rates for their CytoJournal articles, which was achieved with the additional benefit of retaining their copyright in the public domain. These articles will have maximum global scientific impact for future generations. The high citation rates for individual authors additionally benefits them by increasing their H factor and other metrics available free on the web for anyone to monitor.[2]
Finally and most importantly, we thank all the CytoJournal readers for their timely suggestions and preferential citations of CytoJournal articles. We look forward to higher CytoJournal IFs in the future.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
We thank Kathy Rost for secretarial assistance. We also thank Nora Frisch, MD; Romil Nathan; and Anushree Shidham for their copy-editing support.
Available FREE in open access from: http://www.cytojournal.com/text.asp?2013/10/1/18/117359
REFERENCES
- Journal citation reports® (JCR®) impact factor by the Thomson Reuters. Available from: http://wokinfo.com/essays/impact-factor/
- [Google Scholar]
- First cytojournal peer-reviewer's retreat in 2006-Open access, peer-review, and impact factor. Cytojournal. 2006;3:5.
- [Google Scholar]
- Free online availability substantially increases a paper's impact. Nature. 2001;411:521.
- [Google Scholar]
- Comparing the impact of open access (OA) vs. Non-OA articles in the same journals. 2004. D-Lib Mag. :10. Available from: http://www.dlib.org/dlib/june04/harnad/06harnad.html
- [Google Scholar]
- Self-selected or mandated, open access increases citation impact for higher quality research. PLoS One. 2010;5:e13636.
- [Google Scholar]
- The effect of use and access on citations. 2005. Inf Process Manag. :41. Available from: http://www.cfa.harvard.edu/~kurtz/IPM-abstract.html
- [Google Scholar]
- Open access explained!-PHD animation. Available from: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=L5rVH1KGBCY
- [Google Scholar]
- Science in the open, the online home of Cameron Neylon, 2012. On the 10th anniversary of the Budapest declaration. Available from: http://cameronneylon.net/blog/on-the-10th-anniversary-of-the-budapest-declaration/ Archived by WebCite® at http://www.webcitation.org/6ISSTKfrP
- [Google Scholar]
- Berlin declaration on open access to knowledge in the sciences and humanities. Available from: http://freeknowledge.eu/documents/reference/berlin
- [Google Scholar]
- Timeline of the open access movement. Available from: http://oad.simmons.edu/oadwiki/Timeline
- [Google Scholar]
- Thank you Cytojournal reviewers and authors-2008 through 2010. Cytojournal. 2010;7:26.
- [Google Scholar]
- Cytomorphology of cervicovaginal melanoma: ThinPrep versus conventional Papanicolaou tests. Cytojournal. 2010;7:25.
- [Google Scholar]
- Liquid based material from fine needle aspirates from breast carcinomas offers the possibility of long-time storage without significant loss of immunoreactivity of estrogen and progesterone receptors. Cytojournal. 2010;7:24.
- [Google Scholar]
- Compensation crisis related to the onsite adequacy evaluation during FNA procedures-Urgent proactive input from cytopathology community is critical to establish appropriate reimbursement for CPT code 88172 (or its new counterpart if introduced in the future) Cytojournal. 2010;7:23.
- [Google Scholar]
- Adequate reimbursement is crucial to support cost-effective rapid on-site cytopathology evaluations. Cytojournal. 2010;7:22.
- [Google Scholar]
- Determination of HER-2 status on FNAC material from breast carcinomas using in situ hybridization with dual chromogen visualization with silver enhancement (dual SISH) Cytojournal. 2010;7:21.
- [Google Scholar]
- The spectrum of coincident entities with small lymphocytic lymphoma/chronic lymphocytic leukemia (SLL/CLL) diagnosed by cytology. Cytojournal. 2010;7:20.
- [Google Scholar]
- Fine needle aspiration biopsy of an osteoclast-rich undifferentiated urothelial carcinoma: A cytology case report and review of the literature. Cytojournal. 2010;7:18.
- [Google Scholar]
- Pleomorphic adenoma: A diagnostic pitfall in the diagnosis of salivary gland lesions on FNAC: Case reports with review of the literature. Cytojournal. 2010;7:17.
- [Google Scholar]
- Colposcopic evaluation of cervix with persistent inflammatory Pap smear: A prospective analytical study. Cytojournal. 2010;7:16.
- [Google Scholar]
- Evaluation of atypical squamous cells on conventional cytology smears: An experience from a screening program practiced in limited resource settings. Cytojournal. 2010;7:15.
- [Google Scholar]
- Pituitary carcinoma diagnosed on fine needle aspiration: Report of a case and review of pathogenesis. Cytojournal. 2010;7:14.
- [Google Scholar]
- Case study documenting the diagnosis of idiopathic CD4+Lymphocytopenia in a patient with atypical fungal infection (disseminated blastomycosis) by FNA of adrenal mass. Cytojournal. 2010;7:13.
- [Google Scholar]
- Fine needle aspiration diagnosis of Rosai-Dorfman disease in an osteolytic lesion of bone. Cytojournal. 2010;7:12.
- [Google Scholar]
- APTIMA assay on SurePath liquid-based cervical samples compared to endocervical swab samples facilitated by a real time database. Cytojournal. 2010;7:11.
- [Google Scholar]
- Fine-needle aspiration cytology of extra mammary metastatic lesions in the breast: A retrospective study of 36 cases diagnosed during 18 years. Cytojournal. 2010;7:10.
- [Google Scholar]
- Diagnostic difficulties and pitfalls in rapid on-site evaluation of endobronchial ultrasound guided fine needle aspiration. Cytojournal. 2010;7:9.
- [Google Scholar]
- Atypical squamous cells, cannot exclude high grade squamous intraepithelial (ASC-H) in HIV-positive women. Cytojournal. 2010;7:8.
- [Google Scholar]
- Clinical history of HIV infection may be misleading in cytopathology. Cytojournal. 2010;7:7.
- [Google Scholar]
- Progression from on-site to point-of-care fine needle aspiration service: Opportunities and challenges. Cytojournal. 2010;7:6.
- [Google Scholar]
- Fine needle aspiration biopsy diagnosis of dedifferentiated liposarcoma: Cytomorphology and MDM2 amplification by FISH. Cytojournal. 2010;7:5.
- [Google Scholar]
- Cytomorphologic consideration in malignant ascites with renal cell carcinoma: A report of two cases. Cytojournal. 2010;7:4.
- [Google Scholar]
- Integrating a FISH imaging system into the cytology laboratory. Cytojournal. 2010;7:3.
- [Google Scholar]
- A Shandon PapSpin liquid-based gynecological test: A split-sample and direct-to-vial test with histology follow-up study. Cytojournal. 2010;7:2.
- [Google Scholar]
- Two-color immunocytochemistry for evaluation of effusion fluids for metastatic adenocarcinoma. Cytojournal. 2010;7:1.
- [Google Scholar]
- Hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: A diagnostic pitfall in aspiration cytology. Cytojournal. 2010;6:25.
- [Google Scholar]
- Diagnosis and typing of systemic amyloidosis: The role of abdominal fat pad fine needle aspiration biopsy. Cytojournal. 2010;6:24.
- [Google Scholar]
- Testicular touch preparation cytology in the evaluation of male infertility. Cytojournal. 2011;8:24.
- [Google Scholar]
- Cytomorphology of Erdheim-Chester disease presenting as a retroperitoneal soft tissue lesion. Cytojournal. 2011;8:22.
- [Google Scholar]
- Cytological analysis of small branch-duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms provides a more accurate risk assessment of malignancy than symptoms. Cytojournal. 2011;8:21.
- [Google Scholar]
- Utility of on-site evaluation of endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration specimens. Cytojournal. 2011;8:20.
- [Google Scholar]
- Malignancy rate in nondominant nodules in patients with multinodular goiter: Experience with 1,606 cases evaluated by ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration cytology. Cytojournal. 2011;8:19.
- [Google Scholar]
- The cytomorphologic spectrum of small-cell carcinoma and large-cell neuroendocrine carcinoma in body cavity effusions: A study of 68 cases. Cytojournal. 2011;8:18.
- [Google Scholar]
- Cyto-morphological features of extramedullary acute megakaryoblastic leukemia on fine needle aspiration and cerebrospinal fluid cytology: A case report. Cytojournal. 2011;8:17.
- [Google Scholar]
- Salivary duct carcinoma with striking neutrophil-tumor cell cannibalism. Cytojournal. 2011;8:15.
- [Google Scholar]
- Utility of a limited panel of calretinin and Ber-EP4 immunocytochemistry on cytospin preparation of serous effusions: A cost-effective measure in resource-limited settings. Cytojournal. 2011;8:14.
- [Google Scholar]
- A review of uncommon cytopathologic diagnoses of pleural effusions from a chest diseases center in Turkey. Cytojournal. 2011;8:13.
- [Google Scholar]
- A review of the utilization of fine needle aspiration in clinical practice and research in Nigeria. Cytojournal. 2011;8:12.
- [Google Scholar]
- Detection of amyloid in abdominal fat pad aspirates in early amyloidosis: Role of electron microscopy and Congo red stained cell block sections. Cytojournal. 2011;8:11.
- [Google Scholar]
- Endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration biopsy is useful evaluating mediastinal lymphadenopathy in a cancer center. Cytojournal. 2011;8:10.
- [Google Scholar]
- Teenage cervical screening in a high risk American population. Cytojournal. 2011;8:9.
- [Google Scholar]
- Pattern of epithelial cell abnormality in Pap smear: A clinicopathological and demographic correlation. Cytojournal. 2011;8:8.
- [Google Scholar]
- Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration of metastases to the pancreas: A study of 25 cases. Cytojournal. 2011;8:7.
- [Google Scholar]
- Solitary tracheobronchial papilloma: cytomorphology and ancillary studies with histologic correlation. Cytojournal. 2011;8:6.
- [Google Scholar]
- Microfilariae coexisting with a follicular lesion in thyroid aspirate smears in an uncommon case of a retrosternal thyroid mass, clinically presenting as malignancy. Cytojournal. 2011;8:4.
- [Google Scholar]
- Sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy (Rosai-Dorfman Disease): A case report and review of 49 cases with fine needle aspiration cytology. Cytojournal. 2011;8:3.
- [Google Scholar]
- Diagnosis of metastatic fibrolamellar hepatocellular carcinoma by endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration. Cytojournal. 2011;8:2.
- [Google Scholar]
- p16 immunocytochemistry on cell blocks as an adjunct to cervical cytology: Potential reflex testing on specially prepared cell blocks from residual liquid-based cytology specimens. Cytojournal. 2011;8:1.
- [Google Scholar]
- CytoJournal impact factor. 2008-2013 BioxBio.com. Available from: http://www.bioxbio.com/if/html/CYTOJOURNAL.html Archived by WebCite® at http://www.webcitation.org/6ICnd3Cql
- [Google Scholar]
- Acta cytologica impact factor. 2008-2013 BioxBio.com. Available from: http://www.bioxbio.com/if/html/ACTA-CYTOL.html Archived by WebCite® at http://www.webcitation.org/6ICniOhDr
- [Google Scholar]
- Cancer cytopathology impact factor 2008-2013 BioxBio.com. Available from: http://www.bioxbio.com/if/html/CANCER-CYTOPATHOL.html Archived by WebCite® at http://www.webcitation.org/6ICmzjdN3
- [Google Scholar]
- Cytopathology impact factor. 2008-2013 BioxBio.com. Available from: http://www.bioxbio.com/if/html/CYTOPATHOLOGY.html Archived by WebCite® at http://www.webcitation.org/6ICnRJCVR
- [Google Scholar]
- Diagnostic cytopathology impact factor 2008-2013 BioxBio.com. Available from: http://www.bioxbio.com/if/html/DIAGN-CYTOPATHOL.html Archived by WebCite® at http://www.webcitation.org/6ICnYitUD
- [Google Scholar]
- Paraganglioma with unusual presentation in parotid gland: A diagnostic dilemma in fine needle aspiration. Cytojournal. 2012;9:26.
- [Google Scholar]
- Fine needle aspiration-induced vascular proliferation of the thyroid: A report of two cases. Cytojournal. 2012;9:25.
- [Google Scholar]
- Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration of the celiac ganglion: A diagnostic pitfall. Cytojournal. 2012;9:24.
- [Google Scholar]
- Cytomorphology of giant cell tumor of bone in pleural fluid. Cytojournal. 2012;9:22.
- [Google Scholar]
- Metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma presenting as gynecomastia in male: A diagnostic dilema in fine needle aspiration cytology. Cytojournal. 2012;9:21.
- [Google Scholar]
- Prevalence of human papilloma virus in cytological abnormalities: Association of risk factors and cytomorphological findings. Cytojournal. 2012;9:19.
- [Google Scholar]
- Parakeratotic-like cells in effusions: A clue to diagnosis of malignant mesothelioma. Cytojournal. 2012;9:18.
- [Google Scholar]
- Ossifying fibromyxoid tumor-Diagnostic challenge for a cytopathologist. Cytojournal. 2012;9:17.
- [Google Scholar]
- An unusual case of primary effusion lymphoma with aberrant T-cell phenotype in a HIV-negative, HBV-positive, cirrhotic patient, and review of the literature. Cytojournal. 2012;9:16.
- [Google Scholar]
- Cytomorphology of unusual infectious entities in the Pap test. Cytojournal. 2012;9:15.
- [Google Scholar]
- Endoscopic ultrasound and endobronchial ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration of deep-seated lymphadenopathy: Analysis of 1338 cases. Cytojournal. 2012;9:14.
- [Google Scholar]
- Diagnosis of pulmonary hydatid disease presenting with solid nodule and mimicking malignancy by fine needle aspiration cytology. Cytojournal. 2012;9:13.
- [Google Scholar]
- Virtual microscopy in cytotechnology education: Application of knowledge from virtual to glass. Cytojournal. 2012;9:12.
- [Google Scholar]
- A case of clear cell adenocarcinoma arising from the urethral diverticulum: Utility of urinary cytology and immunohistochemistry. Cytojournal. 2012;9:11.
- [Google Scholar]
- Dual color multiplex TTF-1+Napsin A and p63+CK5 immunostaining for subcategorizing of poorly differentiated pulmonary non-small carcinomas into adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma in fine needle aspiration specimens. Cytojournal. 2012;9:10.
- [Google Scholar]
- Cytological diagnosis of metastatic alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma in the ascitic fluid: Report of a case highlighting the diagnostic difficulties. Cytojournal. 2012;9:9.
- [Google Scholar]
- Establishing a protocol for immunocytochemical staining and chromogenic in situ hybridization of Giemsa and diff-quick prestained cytological smears. Cytojournal. 2012;9:8.
- [Google Scholar]
- The Bethesda System thyroid diagnostic categories in the African-American population in conjunction with surgical pathology follow-up. Cytojournal. 2012;9:7.
- [Google Scholar]
- Two smalls in one: Coincident small cell carcinoma and small lymphocytic lymphoma in a lymph node diagnosed by fine-needle aspiration biopsy. Cytojournal. 2012;9:5.
- [Google Scholar]
- Comparative evaluation of the modified Scarff-Bloom-Richardson grading system on breast carcinoma aspirates and histopathology. Cytojournal. 2012;9:4.
- [Google Scholar]
- Comparing endobronchial ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration specimens with and without rapid on-site evaluation. Cytojournal. 2012;9:2.
- [Google Scholar]
- How to write an article: Preparing a publishable manuscript. Cytojournal. 2012;9:1.
- [Google Scholar]
- The creative commons attribution license. Available from: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/20/
- [Google Scholar]
- DOAJ-Directory of open access journals. Available from: http://www.doaj.org/doaj?func=browse and uiLanguage=en
- [Google Scholar]
- Apply for cytopathology foundation (CF) membership. Available from: http://www.cytojournal.comCF member's corner-CFMember.asp
- [Google Scholar]
- Wolters Kluwer Health. Available from: http://www.wolterskluwerhealth.com/pages/welcome.aspx
- [Google Scholar]







